Postman most useful tricks you should know
Introduction
Today, I think Postman and API testing is two unseparable think in most API development environment. Wether you are actually a tester or you are a software developer, Postman is number 1 tool when you deal with API development and testing. Remember that, Abraham Lincoln once said,
“If I had eight hours to chop down a tree, I would spend six of those hours sharpening my axe”
-Abraham Lincoln
Either you are a software tester or a software developer, knowing how to use your tool better is a way to increase your productivity. This article will guide you to maximize the potential of using Postman to increase your productivity by demonstrating daily use case of Postman when dealing with API. You can’t wait to know what is the secret? Here are some secrets I know. If you have one, please share in the comment section.
Secret #1: Create a variable for anything you need
Maybe you have used postman for daily use but always inserting or copy-pasting the url manually every new request. With this tips, you can increase your productivity by decreasing time for copy-pasting or manually inserting the url.
Variable in URI
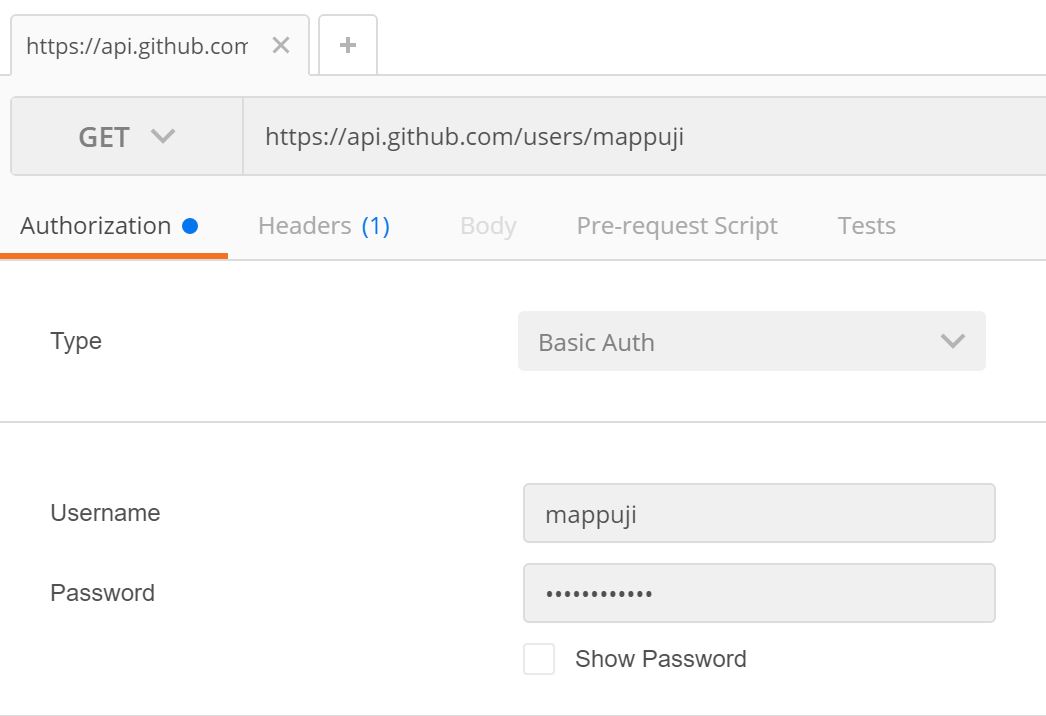
For example we want to try a simple request to GitHub API. It requesting information about me (@empeje). Here are the details. Create a request with the following information.
| Key/Params/Information | Value |
|---|---|
| URI | https://api.github.com/users/empeje |
| Authorization | Basic |
| Username | YourGitHubUsername |
| Password | YourGitHubPassword |
Okay the request would be something like image below.
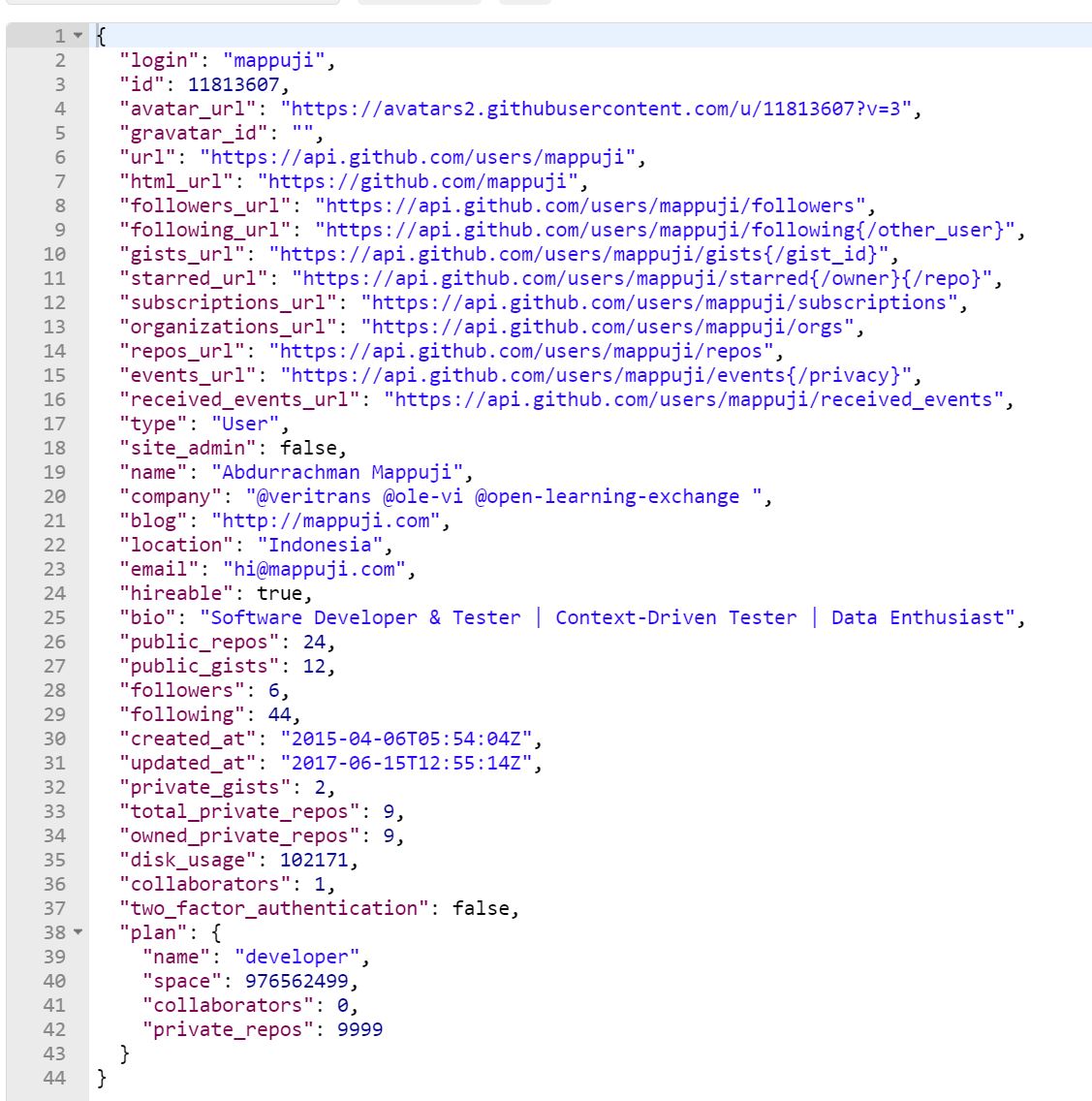
And when you send the request by clicking the Send button you will get something similar to this.
For this kind of simple API, it would be easier for you two manage the Postman Collection, but when you deal with development, staging, and production environment, you will be dealing with many base URI. For example we can call the URI https://api.github.com as production URI of GitHub API, but for the GitHub development team, they may have many environment like development, staging, and production with different base URI. In that case, you need to automate your workflow by defining a variable/constant in Postman Environment.
Click something in the top right of Postman windows, below the user section. You will have some choices about environment, when you haven’t yet created an environment, you only have No Environment options. The UI would be something like this.
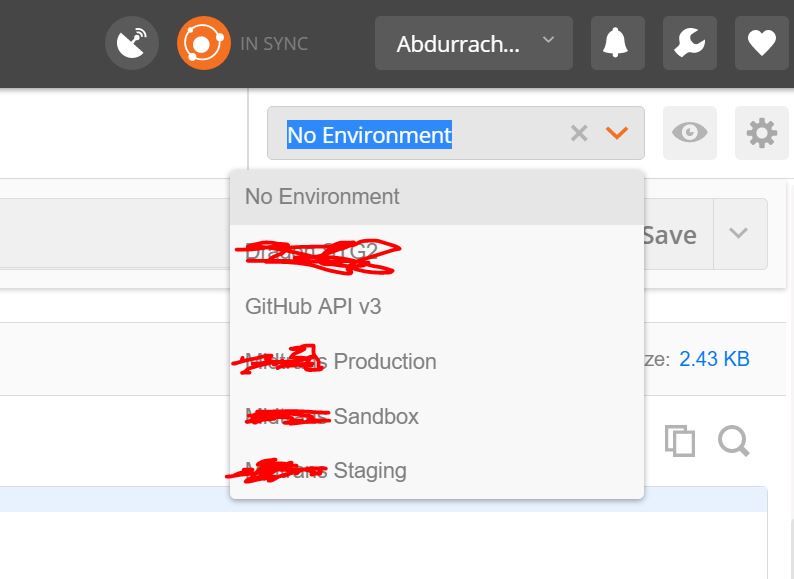
Click Gear then click Manage Environment button to manage your environment and you will have something like this.
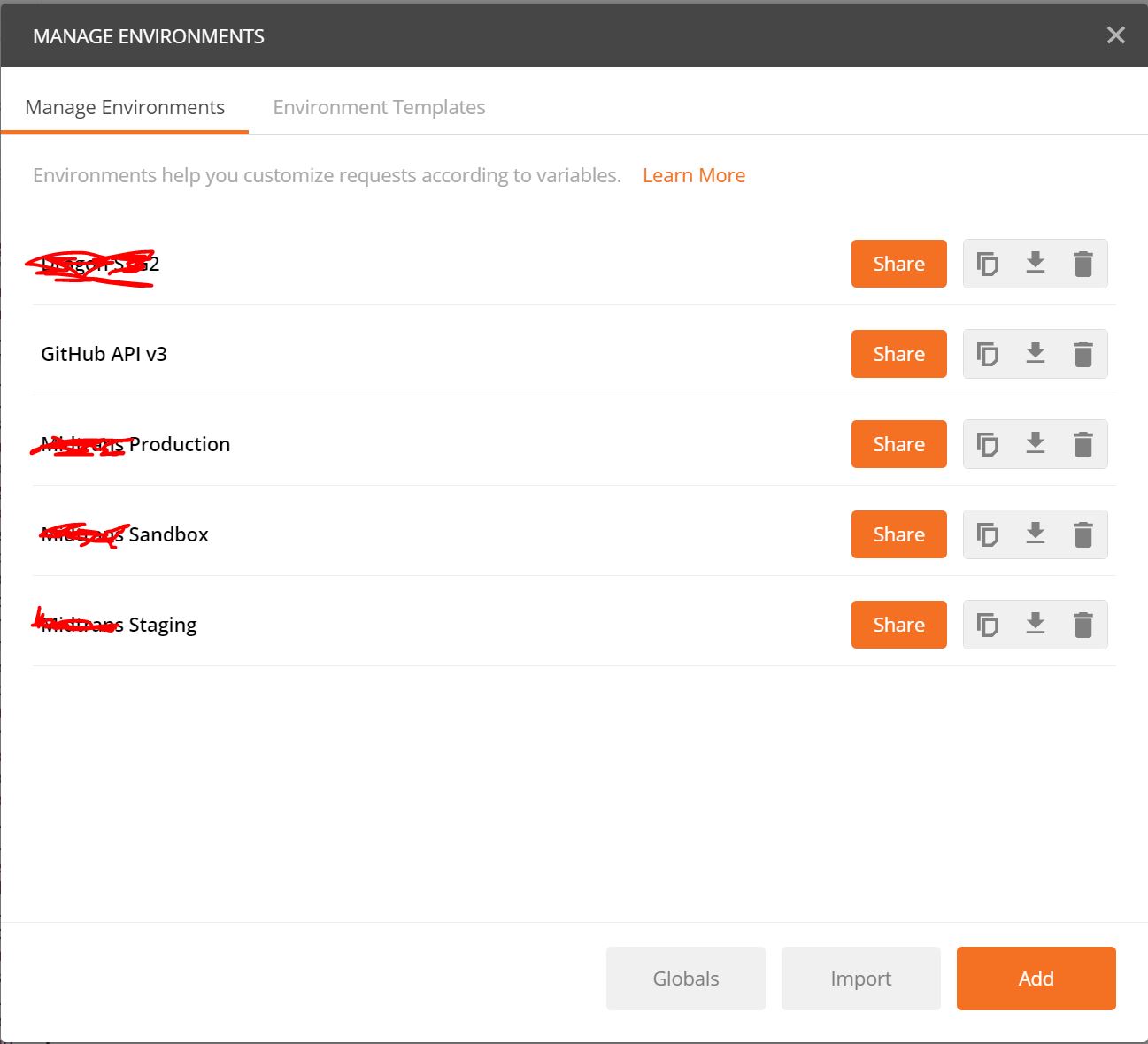
Then click orange Add button to create new environment. In environment you could have a key-value pair which act like a constant, but you can edit it in runtime which we can talk about it later. Lets call it environment variable. You can have different environtment with different list of key-value pair, for your purpose. So, you can change many parameter value automagically by only changing the environment you want to use.
Lets put a key called url with value https://api.github.com and give it a name Engineer in Test so you can use it as a base url. The result would be like this.
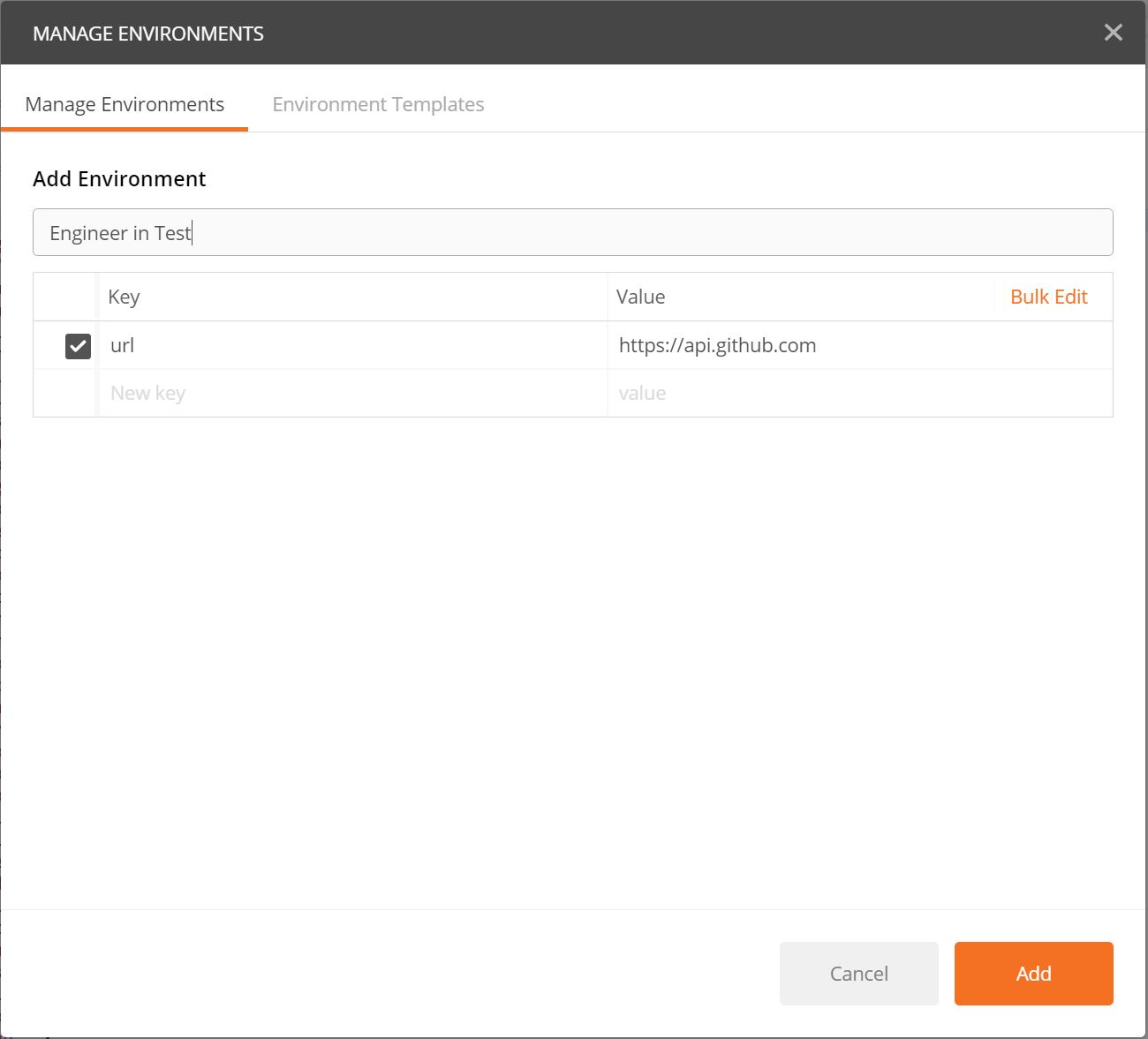
Click Add and close Manage Environment windows. Now, you can use your environment by changing environment to Engineer in Test. So, in order to make the environment variable useful, change the URI from https://api.github.com/users/empeje to { { url } }/users/empeje without space. So, the result would be like this.
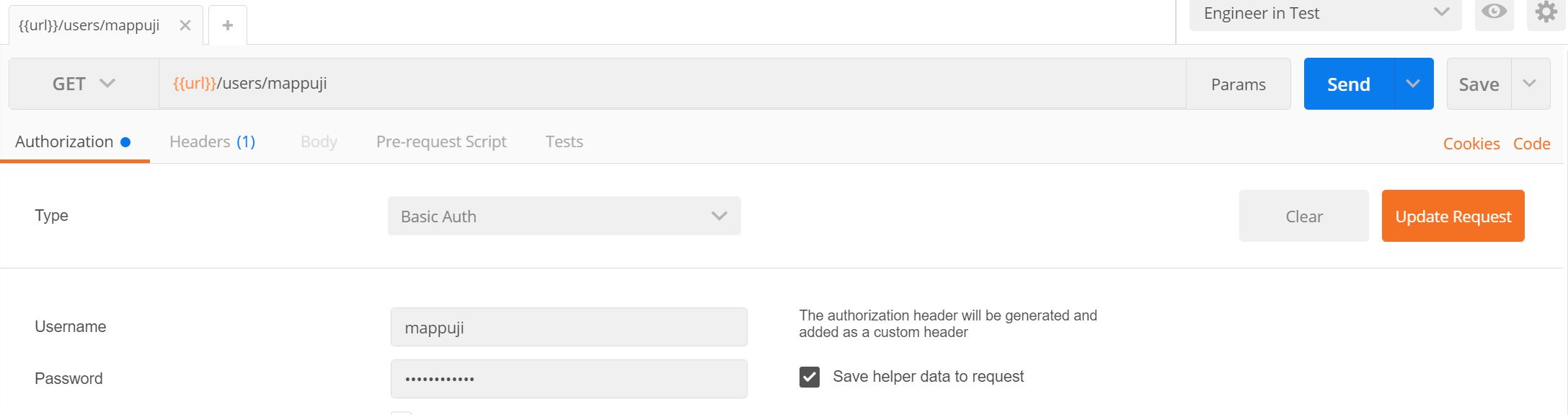
And when you send the request, the result would be the same :D
Variable also works in HTTP Header, Params, and Body Request, and almost anything
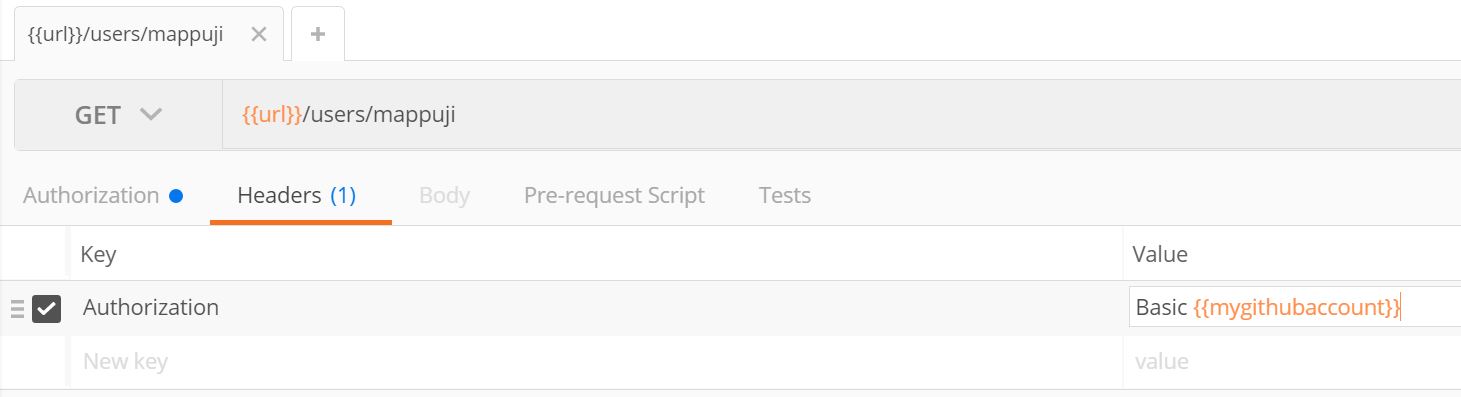
Okay you already create a key-value pair of environment variable for your URI, lets create something for your Authorization. Now, I want to create username and password for my environment. I copy the encrypted value of username and password from Authorization tab, and create a variable for it.
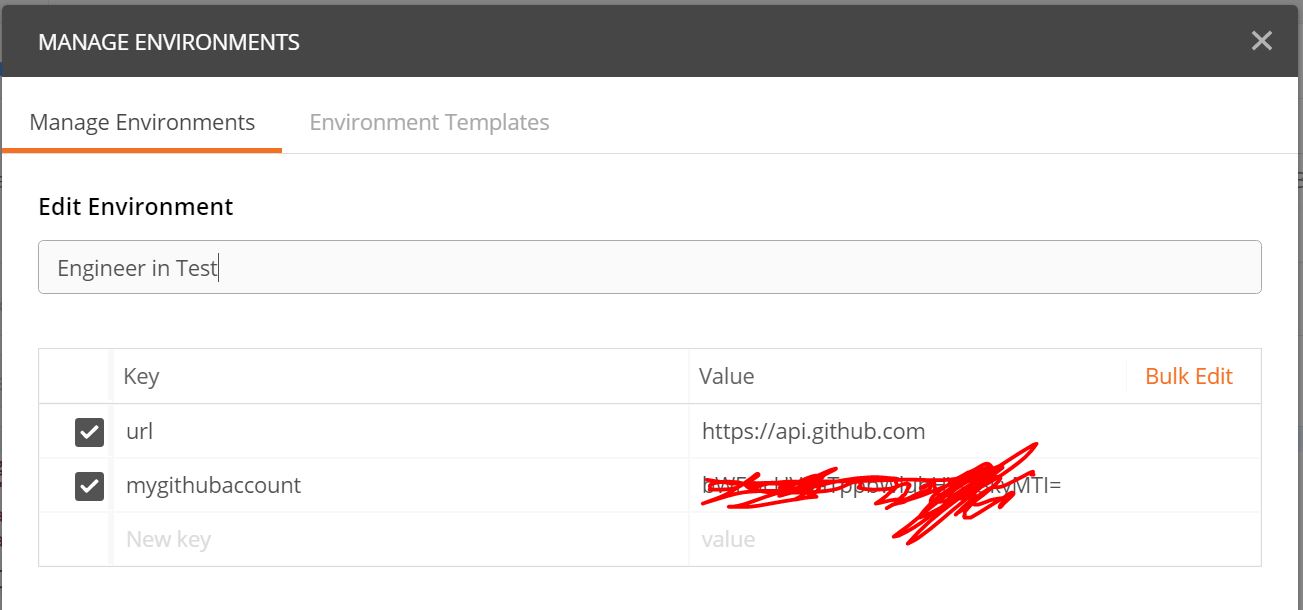
And I use it like this.
Use pre-defined variable of postman to unique key
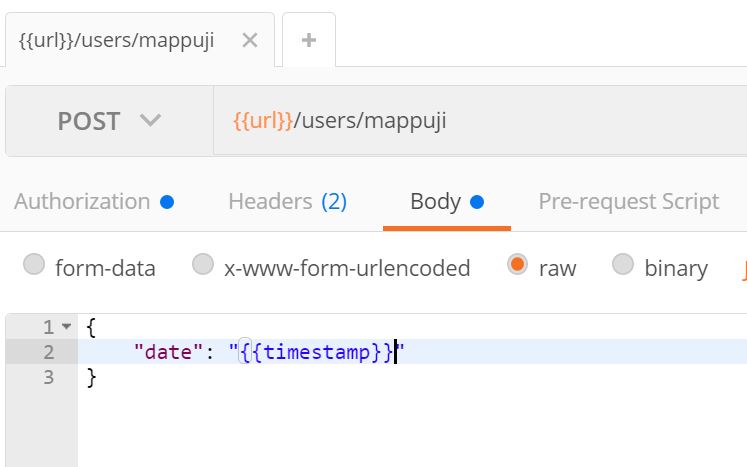
Postman comes with predefined dynamic variable as shown below. Remember to delete space in the variable I’ve mentioned.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
{ { $guid } } |
Adds a v4 style guid |
{ { $timestamp } } |
Adds the current timestamps |
{ { $randomInt } } |
Adds a random integer between 0 and 1000 |
And use it like this.
Use current result as next input by saving to variable
There is some case you want to get a token in one endpoint and use that token in other endpoint. While it is kinda annoying when you have to type or copy-paste it manually, postman help you to do it automagically.
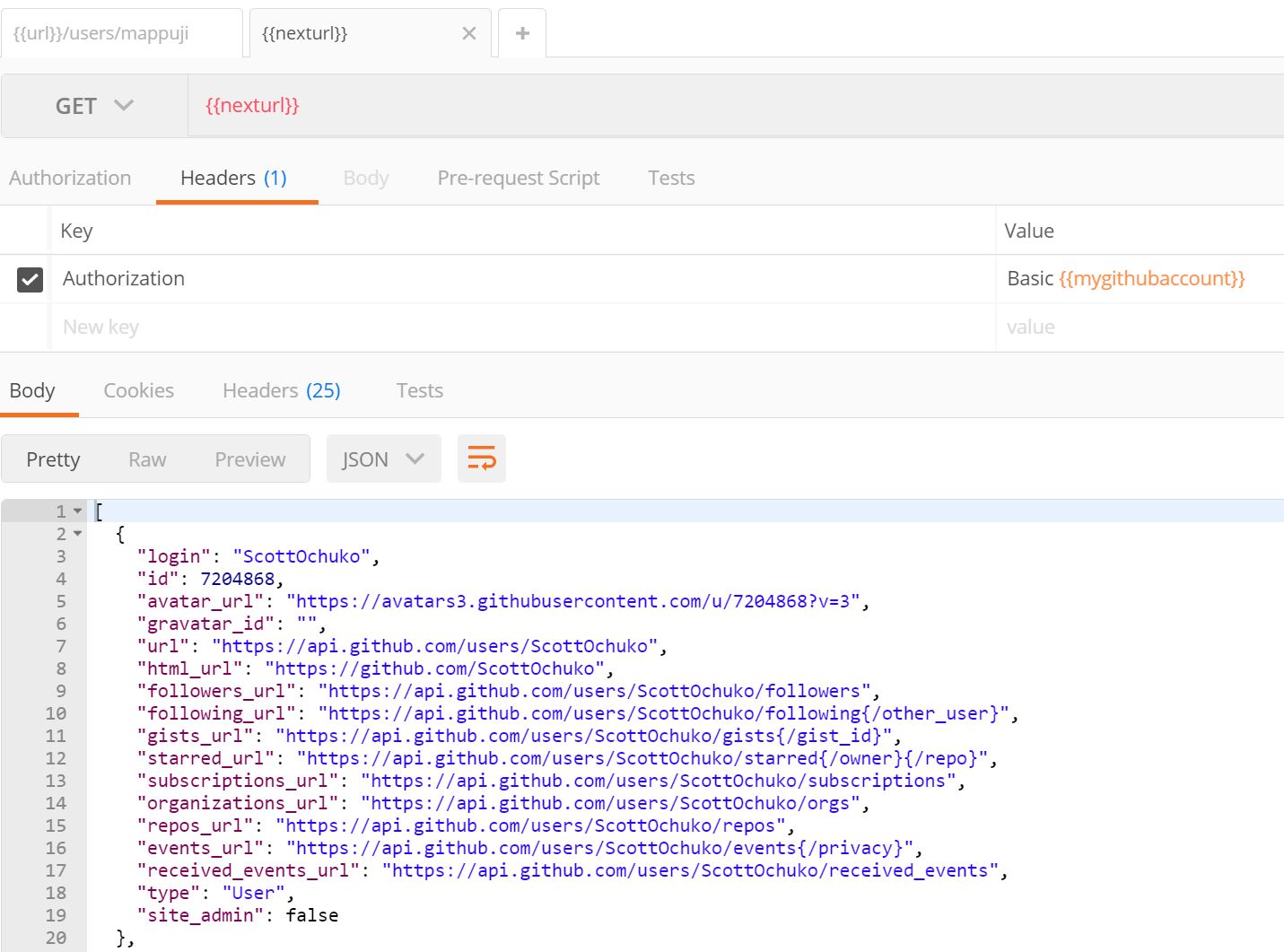
Perhaps I want see my followers as the next url, what I want to do is I click Test section in the request tab, and write the following.
var jsonData = JSON.parse(responseBody);
postman.setEnvironmentVariable("nexturl", jsonData.followers_url);
It is basically extract the key followers_url from response body and save it as environment varibale called nexturl.
Now you can click Send to send the request. Then move to our nexturl request and you can hava a simple uri like this.
Conclusion
The use of variable in Postman is a thing you should know when you deal with many environment and API development both for hobby or your daily professional workflow. Hope you enjoy the article and see you in Part 2 of this article.