How to setup Redis in Kubernetes
Recently I getting involved in Kubernetes when setting up a test cluster (test infrastructure) for a project in my current company. It is pretty interesting how easy we orchestrate and organize our software infrastructure with Kubernetes.
Here I will share abou how I setup Redis in Kubernetes by taking example installing it in Minikube.
Prerequisite
- Kubernetes kluster (Minikube will work)
- YAML script for redis I describe here in empeje/redis-k8s
Notes for impatience
Go directly to the TL;DR in the bottom if you want to go-to way.
Let’s go!
Basically in Kubernetes there is some resources we can leverage, several of them are
- Pods
- ReplicationControllers
- Services
- Deployments
- ConfigMaps
- etc
I will not cover everything, but we will know about pods, replication controllers, services, deployments, and config maps. Suppose we want to setup a redis cluster with one master and one sentinel. We also want to setup redis config via config map, a resource that can generate config in the container for use either it is in form of environment variable or it is a file.
First let’s start with the config map. In Kubernetes we can have declarative script either in yaml or in json format, but in this case I will use yaml since it is more common and more human readable.
Suppose we want to add the following config for our Redis config.
bind 0.0.0.0
The example of config map setup in yaml is the following.
configmap.yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
redis-config: |
bind 0.0.0.0
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
labels:
name: example-redis-configmap
name: example-redis
In the above script we will add a config map key called redis-config with value bind 0.0.0.0. We also tell the Kubernetes that this yaml is for ConfigMap with kind: ConfigMap. We also add labels metadata for future reference and name for accessing the config map.
Suppose you save the file as configmap.yaml. You can setup the config map by
> kubectl create -f configmap.yaml
configmap "example-redis" created
And you can check that your config map is there by
>kubectl get configmap
NAME DATA AGE
example-redis 1 10s
Having you already setup the config map, now you can setup deployment and service resources. Below are the example I use to setup the Redis. You can also visit my GitHub repository I mentioned above to download everything.
deployment.yaml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
name: example-redis-svc
role: service
name: example-redis
spec:
ports:
- port: 6379
targetPort: 6379
selector:
role: redis-master
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
name: example-redis-sentinel-svc
role: service
name: example-redis-sentinel
spec:
ports:
- port: 26379
targetPort: 26379
selector:
role: redis-sentinel
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
name: example-redis-deploy
name: example-redis
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: example-redis
role: redis-master
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: example-redis
role: redis-master
spec:
containers:
- image: k8s.gcr.io/redis:v1
name: example-redis
env:
- name: MASTER
value: "true"
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /redis-master-data
name: data
- mountPath: /redis-master
name: config
volumes:
- name: data
emptyDir: {}
- name: config
configMap:
name: example-redis
items:
- key: redis-config
path: redis.conf
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
name: example-redis-sentinel-deploy
name: example-redis-sentinel
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: example-redis-sentinel
role: redis-sentinel
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: example-redis-sentinel
role: redis-sentinel
spec:
containers:
- image: k8s.gcr.io/redis:v1
name: example-redis-sentinel
env:
- name: SENTINEL
value: "true"
ports:
- containerPort: 26379
In above setup, we setup deployment and service resources both for Redis master and Redis sentinel. In Redis master we add config map which ask for redis-config key in example-redis config map.
Then you can setup the deployment and service by running the following commands
> kubectl create -f deployment.yaml
service "example-redis" created
service "example-redis-sentinel" created
deployment "example-redis" created
deployment "example-redis-sentinel" created
And then verify
> kubectl get all
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deploy/example-redis 1 1 1 1 7s
deploy/example-redis-sentinel 1 1 1 1 7s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
rs/example-redis-f55fddff6 1 1 1 7s
rs/example-redis-sentinel-bf477fd4 1 1 1 7s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deploy/example-redis 1 1 1 1 7s
deploy/example-redis-sentinel 1 1 1 1 7s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
rs/example-redis-f55fddff6 1 1 1 7s
rs/example-redis-sentinel-bf477fd4 1 1 1 7s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
po/example-redis-f55fddff6-62mgr 1/1 Running 0 7s
po/example-redis-sentinel-bf477fd4-fpztw 1/1 Running 0 7s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
svc/example-redis ClusterIP 10.106.233.108 <none> 6379/TCP 7s
svc/example-redis-sentinel ClusterIP 10.98.82.139 <none> 26379/TCP 7s
svc/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 4h
And try to access via redis-cli
>kubectl run -it --rm --image=redis --restart=Never redis-client13 -- redis-cli -h example-redis -p 6379
If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter.
example-redis:6379>
example-redis:6379> exit
You can also access the UI dashboard by
> minikube dashboard
Opening kubernetes dashboard in default browser...
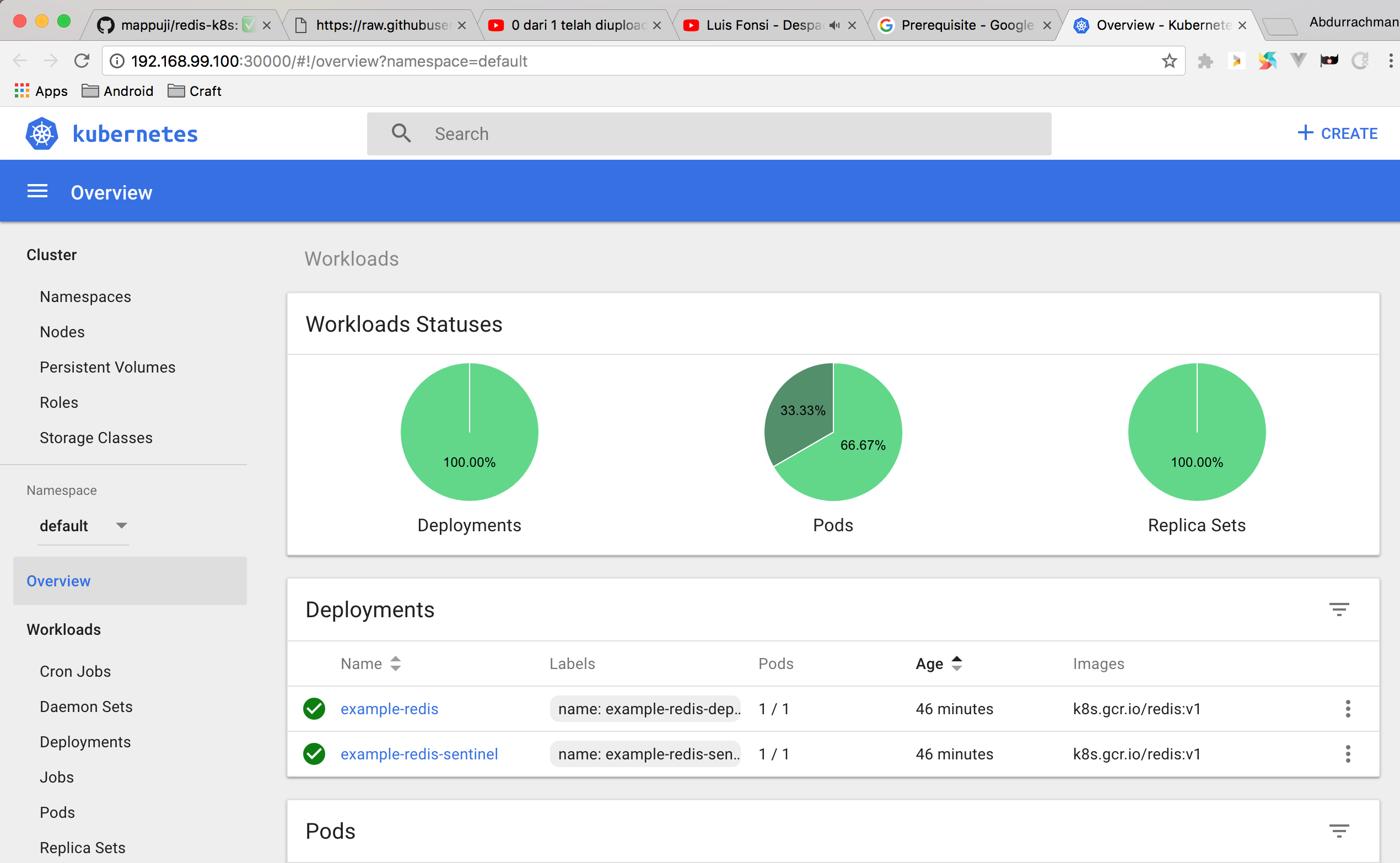
Pretty handy and straightforward right?
Last heere is the TL;DR.
TL;DR
# setup configmap
kubectl create -f configmap.yaml
# setup deployment
kubectl create -f deployment.yaml
# check
kubectl get all
# wait until all running
kubectl run -it --rm --image=redis --restart=Never redis-client-example -- redis-cli -h example-redis -p 6379
Conclusion
In this article we demonstrate how to setup Redis in Kubernetes cluster using deployment, services and ConfigMap resources.